Junction Block options for Zaber Nucleus microscopes
By Mike Fussell, Life Sciences Product Manager
Published on Dec. 18, 2025
Many applications require an additional port into or out of the infinity space. This may be to inject a laser into the optical path (e.g. excitation-based) or to divert light out of it to a secondary detector (e.g. emission-based). The MJB25 adds an additional dichroic mirror/beam splitter and filter between the filter cube and the objective. Filters can be secured using an SM1 retaining ring.

Figure 1. Location of the MJB25B on an MKR microscope Core
To accommodate the MJB25, the X-LDA focus stage on an MKR core must be raised by 35 mm relative to its standard location. The additional distance between the objective lens and filter cube may result in vignetting (reduced intensity near the periphery of the image) when high N.A. (0.80 or greater) objective lenses are used. For upright microscopes, the MKR025B microscope core module is set with the additional 35mm of spacing to accommodate the MJB25. The MKR025D provides the additional 35mm spacing on upright configurations.
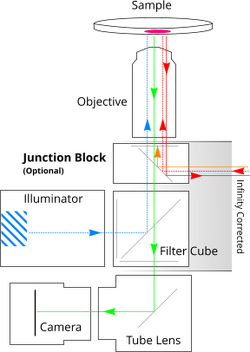
Figure 2. Schematic of MVR optical path showing positions of additional dichroic and filter added with the MJB25 junction block.
| Filter Position | Filter Mounting | Max. Filter Dimensions | Part Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper | SM1 Lock Ring | 25.4 mm x 1 mm | MJB25A |
Table 1. Comparison of junction block modules
Autofocus-Specific Junction Block
The MJB25C-F1 is required for configurations including the HL04 laser autofocus sensor. The MJB25C-F1 houses the required 785 nm notch filter which couples the laser from the AF sensor to the optical path.