T-Series/Compilation/Commands for T-CD
Detailed Command Reference
This command reference applies only to firmware version 5.00 and up to the most recent version. The version of firmware installed on any Zaber T-Series device can be determined by issuing command #51. A three-digit number will be returned. Assume 2 decimal places (ex a reply of 293 indicates firmware version 2.93). For earlier versions of firmware, please consult the appropriate PDF user's manual:
Due to the addition of new features, newer versions of firmware may not be 100% backward compatible. You may wish to read the document Firmware History and Migration which outlines the changes that have taken place from one firmware version to the next and indicates what options are available if you wish to upgrade or downgrade the firmware on your devices.
Reset - Cmd 0
| Instruction Name | Reset |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All Zaber devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.00 and up |
| Command Number | 0 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Ignored |
| Reply Data | None |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Sets the device to its power-up condition. |
This has the same effect as unplugging and restarting the device.
Home - Cmd 1
| Instruction Name | Home |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 1 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Ignored |
| Reply Data | Final Position |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | Yes |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Moves to the home position and resets the device's internal position. |
Upon receiving this instruction, the device will retract until its internal home sensor is triggered. It will then move forward several steps to avoid accidentally re-triggering the home sensor during use. Its internal position is then reset (to 0 for most devices). If a home offset has been specified with the Set Home Offset (cmd 47) instruction, the device will move forward for the specific offset, then reset the internal position.
Prior to Firmware 5.21, the device will attempt to home for an extended amount of time. For Firmware 5.21 and up, the home command aborts with an error if the device has traveled twice the Maximum Position setting without triggering the home sensor. This indicates that the device could possibly be stalling or slipping.
Renumber - Cmd 2
| Instruction Name | Renumber |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All Zaber devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.00 and up |
| Command Number | 2 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | New Number |
| Reply Data | Device ID |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Assigns new numbers to all the devices in the order in which they are connected. |
This command is usually sent to device number 0. When it is, the command data is ignored and all devices will renumber. The device closest to the computer becomes device number 1. The next device becomes number 2 and so on.
If sent to a device number other than 0, then that device will reassign itself the device number in the command data. Valid device numbers are 1-99 for version 6.05, and 1-254 otherwise.
Note: Renumbering takes about 1/2 a second during which time the computer must not send any further data. The device number is stored in non-volatile memory so you can renumber once and not worry about issuing the renumber instruction again after each power-up.
Store Current Position - Cmd 16
| Instruction Name | Store Current Position |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.04 and up |
| Command Number | 16 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Address |
| Reply Data | Address |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Saves the current absolute position of the device. |
Valid Address values are 0 through 15 specifying one of 16 possible registers in which to store the position. This command can only be executed when the device has been homed. This command is used in conjunction with the Return Stored Position (Command #17) and Move To Stored Position (Command #18) instructions. The positions stored in the position registers are non-volatile and will persist after power-down or reset. All position registers are cleared by the Restore Settings (Command #36) instruction.
Return Stored Position - Cmd 17
| Instruction Name | Return Stored Position |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.04 and up |
| Command Number | 17 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Address |
| Reply Data | Stored Position |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Returns the position stored in one of the 16 position registers for the device. |
Valid command data values are 0 through 15, specifying one of 16 possible registers from which to retrieve the position. This command is used in conjunction with the Store Current Position (#16) and Move To Stored Position (#18) commands. Positions stored in the position registers are non-volatile and will persist after power-down or reset. All position registers are cleared by the Restore Settings (#36) command.
Move To Stored Position - Cmd 18
| Instruction Name | Move To Stored Position |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.04 and up |
| Command Number | 18 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Address |
| Reply Data | Final Position |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | Yes |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Moves the device to the stored position specified by the Command Data. |
Valid address values are 0 through 15, specifying one of 16 possible positions. This command is used in conjunction with the Store Current Position (#16) and Return Stored Position (#17) commands. This command does not send a response until the move has finished. All move commands are pre-emptive. If a new move command is issued before the previous move command is finished, the device will immediately move to the new position.
The target speed and acceleration during a move absolute instruction can be specified using Set Target Speed (Cmd 42) and Set Acceleration (Cmd 43) respectively.
This command may pre-empt, or be pre-empted by Move to Stored Position (Cmd 18), Move Absolute (Cmd 20), Move Relative (Cmd 21), Move at Constant Speed (Cmd 22), Move Index (Cmd 78) and Stop (Cmd 23).
Move Absolute - Cmd 20
| Instruction Name | Move Absolute |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 20 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Absolute Position |
| Reply Data | Final Position |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | Yes |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Moves the device to the position specified in the Command Data in microsteps. |
The device begins to move immediately, and sends a response when the move has finished. The position must be between 0 and Maximum Position (specified by Set Maximum Position (cmd 44)), or an error code will be returned.
The target speed and acceleration during a move absolute instruction can be specified using Set Target Speed (Cmd 42) and Set Acceleration (Cmd 43) respectively.
All move commands are pre-emptive. If a new move command is issued before the previous move command is finished, the device will immediately move to the new position. This command may pre-empt, or be pre-empted by Move to Stored Position (Cmd 18), Move Absolute (Cmd 20), Move Relative (Cmd 21), Move at Constant Speed (Cmd 22) and Stop (Cmd 23).
Move Relative - Cmd 21
| Instruction Name | Move Relative |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 21 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Relative Position |
| Reply Data | Final Position |
| Safe to retry? | No |
| Returns Current Position? | Yes |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Moves the device by the positive or negative number of microsteps specified in the Command Data. |
The device moves to a position given by its current position plus the value specified in the command data. The relative move command data in microsteps can be positive or negative. The final position must be between 0 and Maximum Position (specified by Set Maximum Position (cmd 44)), or an error code will be returned. The device begins to move immediately, and sends a response when the move has finished.
The target speed and acceleration during a move absolute instruction can be specified using Set Target Speed (Cmd 42) and Set Acceleration (Cmd 43) respectively.
All move commands are pre-emptive. If a new move command is issued before the previous move command is finished, the device will immediately move to the new position. If a Move Relative command is issued while the device is currently moving due to a previous command, the device will immediately set a new target position equal to the current position (at the instant the command was received) plus the specified relative position.
This command may pre-empt, or be pre-empted by Move to Stored Position (Cmd 18), Move Absolute (Cmd 20), Move Relative (Cmd 21), Move at Constant Speed (Cmd 22) and Stop (Cmd 23).
Move At Constant Speed - Cmd 22
| Instruction Name | Move At Constant Speed |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 22 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Speed |
| Reply Data | Speed |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Moves the device at a constant speed based on the value specified in the Command Data. |
This instruction specifies a direction and a speed to move, rather than a target position. When this instruction is issued the device will accelerate (at a rate determined by command #43 Set Acceleration) to the speed specified by the instruction data. The device will continue moving at this speed until a limit is reached or a pre-empting instruction is issued. Negative speeds cause retraction while positive speeds cause extension. Unlike the other movement commands, this command sends a response immediately without waiting for the move to finish.
The device may be set to return its position continuously during the move using the set mode command (#40)] bit 4. Position tracking is a reply-only command #8. If the device runs into zero position or maximum range, the device stops and the new position is returned via reply-only command #9.
This command may pre-empt, or be pre-empted by commands 18, 20, 21, 22 and 23.
For a spreadsheet that can be used to calculate speed setting values for any product see https://www.zaber.com/documents/ZaberSpeedSetting.xls. Alternatively you may use the formulas below.
Actual Speed
- = Data * 9.375 * M mm/s or deg/s
- = Data * 9.375 microsteps/s
- = Data * 9.375 / R steps/s
- = Data * 9.375 / (R x S) * 60 revolutions/min Motor rpm
- = Data * 9.375 * L / (R x S) mm/s Linear devices only
where:
- Data is the value of the command data
- R (microsteps/step) is the microstep resolution (command 37)
- S (steps/revolution) is the number of steps per motor revolution
- M (mm or deg) is the microstep size
- L (mm or deg) is the distance of linear motion per motor revolution
Refer to product specifications for the distance corresponding to a single microstep or revolution.
For example, if a motor has 48 steps per revolution (S = 48), used with default resolution (R = 64), and Data is 2922, then the motor will move at a speed of approximately 535 revolutions per minute.
Valid data values are from (−512×R−1) to (512×R−1). Note that a value of zero will cause the device to decelerate to a stop and then send Limit Active (Cmd 9).
Stop - Cmd 23
| Instruction Name | Stop |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 23 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Ignored |
| Reply Data | Final Position |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | Yes |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Stops the device from moving by preempting any move instruction. |
This instruction can be used to pre-empt any move instruction. The device will decelerate to a stop. The reply data is the absolute position after stopping.
The device will decelerate at a rate specified by Set Acceleration (Cmd 43).
This command may pre-empt, or be pre-empted by Move to Stored Position (Cmd 18), Move Absolute (Cmd 20), Move Relative (Cmd 21), Move at Constant Speed (Cmd 22) and Stop (Cmd 23).
Read Or Write Memory - Cmd 35
| Instruction Name | Read Or Write Memory |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 35 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Data |
| Reply Data | Data |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Reads or writes a byte of non-volatile memory. |
128 bytes of memory are available for user data. For example, the user may want to save some custom data such as a serial number, a name string, or data that uniquely identifies a particular device. Data written is not cleared by power down or reset. The most significant bit of byte 3 specifies whether the instruction is a read (0) or a write (1). The least significant 7 bits of byte 3 specify the address to read/write (0 to 127). Byte 4 specifies the value to be written. Bytes 5 and 6 are ignored.
These settings are stored in non-volatile memory and will persist after power-down or reset.
Restore Settings - Cmd 36
| Instruction Name | Restore Settings |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-CD |
| Firmware Version | 5.00 and up |
| Command Number | 36 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Peripheral ID |
| Reply Data | Peripheral ID |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Restores the device settings to the factory defaults. |
This command should be issued with a Peripheral ID of 0 to return the device to factory default settings. This instruction is very useful for troubleshooting. If the device does not appear to function properly, it may be because some of the settings have been changed. This instruction will restore the settings to default values. For a table of default settings, see Appendix A. All settings affected by this instruction are stored in non-volatile memory and will persist after power-down or reset.
Peripheral IDs
The T-CD motor controller is designed to control many different motors and actuators. The Restore Settings instruction should usually be issued with a Peripheral ID corresponding to the specific motor or motorized device connected. This will set the T-CD motor controller to the factory default settings for the motorized peripheral in question. For example, if a T-CD device is connected to an NA11B30, the user can issue the Restore Settings instruction with a Peripheral ID of 31130. This will automatically set all non-volatile parameters (range, mode, running and hold currents, etc) to values that will work with the NA11B30.
The table below shows Peripheral IDs for all Zaber products compatible with T-CD devices. Note that some of these products may be discontinued. For a list of settings corresponding to each of these Peripheral IDs, see https://www.zaber.com/device-settings.
| LM Series | NA Series | NM Series |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
'*' These peripheral IDs are only valid on T-CD2500 (not on T-CD1000) because these devices require more than 1000mA/phase driving current.
If the Restore Settings instruction is issued with data of 0 rather than one of the above peripheral IDs, then the T-CD device will be set to its lowest running current possible. This is the safest setting that prevents damage to any motor connected to the T-CD, but as a result, you will likely not be able to run a motor with the T-CD set to this condition. You can either issue the Restore Settings instruction with one of the peripheral IDs listed above, or you can adjust each relevant setting independently. Note that the default settings for a given peripheral ID are just a starting point to get your device working. The settings should still be adjusted individually for optimum performance in your application.
Set Microstep Resolution - Cmd 37
| Instruction Name | Set Microstep Resolution |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 37 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Microsteps |
| Reply Data | Microsteps |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Changes the number of microsteps per step. |
This command sets the microstep resolution of a device.
This setting is stored in non-volatile memory and will persist after power-down or reset. Use Restore Settings (Cmd 36) to restore all non-volatile settings to factory default.
The default on most devices is 64. Available microstep resolutions are:
- 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128
All position data sent to or received from T-Series products is in units of microsteps. Note that when you change the microstep resolution, other position related settings are scaled automatically from current values to adjust for the new microstep size. The table below gives an example showing how other settings are affected when the microstep resolution is changed from 128 to 64:
| Setting | Before | After |
| Target Speed * | 2922 | 1461 |
| Maximum Travel Range * | 280000 | 140000 |
| Current Position | 10501 ** | 5250 ** |
| Maximum Relative Move * | 20000 | 10000 |
| Home Offset * | 1000 | 500 |
| Acceleration * | 100 | 50 |
* The settings for these commands are saved in non-volatile memory.
** Note that if a number is divided by two, it is rounded down to the nearest whole number. The only exception to this is if acceleration would become 0 (because 0 for acceleration indicates infinite acceleration). If acceleration would become 0, it will instead be set to 1 which is the lowest acceleration possible.
Set Running Current - Cmd 38
| Instruction Name | Set Running Current |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-series motorized devices (excluding T-LSQ, T-LST, T-MCA) |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 38 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Value |
| Reply Data | Value |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Sets the desired current to be used when the device is moving. |
If your application does not require high torque, it is best to decrease the driving current to reduce power consumption, vibration, and motor heating. Trial and error should suggest an appropriate setting. If higher torque is required, it is generally safe to overdrive motors as long as they are not operated continuously. Motor temperature is typically the best indication of the degree to which overdriving can be employed. If the motor gets too hot to touch (>75°C), you should reduce the running current.
The current is related to the data by the formula:
- Current = CurrentCapacity * 10 / CommandData
The range of accepted values is 0 (no current), 10 (max) - 127 (min). CurrentCapacity is the hardware's maximum capability of output current.
To prevent damage, some devices limit the maximum output current to a lower value. In that case the valid range is 0, Limit - 127. Current limits are listed under the device specifications.
Some devices limit the voltage rather than the current. In this case the same formula can be used by replacing Current and CurrentCapacity with Voltage and PowerSupplyVoltage.
For example, Suppose you connect a stepper motor rated for 420mA per phase to a T-CD2500. Reversing the equation above and using 420mA as Current gives:
CommandData
- = 10 * CurrentCapacity / Current
- = 10 * 2500mA / 420mA
- = 59.5 (round to 60)
Therefore CommandData = 60.
Set Hold Current - Cmd 39
| Instruction Name | Set Hold Current |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-series motorized devices (excluding T-LSQ, T-LST, T-MCA) |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 39 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Value |
| Reply Data | Value |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Sets the desired current to be used when the device is holding its position. |
It is typical to run stepper motors at their rated current only during moves (for highest torque) and reduce the current when idle just to hold the position.
Typically the hold current can be set to around 25 - 50% of the running current. In some applications, the friction of the drive system alone is sufficient to hold the microstep position of the motor, and the hold current can be turned off completely. The hold current can be turned off by issuing the "Set Hold Current" instruction with data of 0.
When the device is moving, it applies running current to the motor. When the device stops moving, running current is applied for an additional 0.1 second before hold current is applied.
The current is related to the data by the formula:
- Current = CurrentCapacity * 10 / CommandData
The range of accepted values is 0 (no current), 10 (max) - 127 (min). CurrentCapacity is the hardware's maximum capability of output current.
To prevent damage, some devices limit the maximum output current to a lower value. In that case the valid range is 0, Limit - 127. Current limits are listed under the device specifications.
Some devices limit the voltage rather than the current. In this case the same formula can be used by replacing Current and CurrentCapacity with Voltage and PowerSupplyVoltage.
For example, Suppose you connect a stepper motor rated for 420mA per phase to a T-CD2500. Reversing the equation above and using 420mA as Current gives:
CommandData
- = 10 * CurrentCapacity / Current
- = 10 * 2500mA / 420mA
- = 59.5 (round to 60)
Therefore CommandData = 60.
Set Device Mode - Cmd 40
| Instruction Name | Set Device Mode |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-CD |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx since 5.04 |
| Command Number | 40 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Mode |
| Reply Data | Mode |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Sets the Mode for the given device. |
Precaution: T-CD devices can accept a variety of motors and home sensors. On these devices, bit 12 may need to be changed from the default setting in order for the home sensor to function correctly. Damage to the home sensor or actuator may result if this bit is set improperly.
This command allows setting several options. Each option is controlled by a single bit within the command data. Most software you will encounter, including most of our demo software, represents all 4 data bytes as a single decimal value rather than specifying each bit individually. To determine what decimal value to use requires a basic understanding of how the data is represented in binary. The command data may be considered as a single 32-bit binary value. The least significant bit is bit_0, the next is bit_1, the next is bit_2, and so on up to the most significant bit_31. Each bit may have a value of either 1 or 0.
The corresponding decimal representation of this 32-bit data is given by:
Decimal value = (bit_0 * 1) + (bit_1 * 2) + … + (bit_n * 2^n) + … + (bit_31 * 2^31)
Each bit controls a single mode option as described in the table below. To determine the data value to use with the Set Device Mode command, simply determine the desired value of each bit (1 or 0), and calculate the decimal value using the above formula. Note that not all 32 bits are currently used. Any unused or reserved bits should be left as 0.
For example, suppose you want all mode bits to be 0 except for bit_3 (disable potentiometer), bit_14 (disable power LED), and bit_15 (disable serial LED). The Set Device Mode instruction should be sent with data calculated as follows:
Command Data = 2^23 + 2^214 + 2^215
= 8 + 16384 + 32768
= 49160
Note that each instance of the Set Device Mode command overwrites ALL previous mode bits. Repeated commands do not have a cumulative effect. For example, suppose you send a Set Device Mode command with data of 8 to disable the potentiometer. If you then send another Set Device Mode command with data of 16384 to disable the power LED, you will re-enabled the potentiometer since bit_3 in the 2nd instruction is 0.
Most devices have a default mode setting of 0 (all bits are 0), however, there are some exceptions. See T-Series/Device IDs and Default Settings for a table of default settings for all devices.
| Bit_n | 2^n | Description
|
| bit_0 | 1 | Disable Auto-reply A value of 1 disables ALL replies except those to “echo”, “read”, “renumber”, and “return” commands. The default value is 0 on all devices. |
| bit_1 | 2 | Enable Anti-backlash Routine A value of 1 enables anti-backlash. On negative moves (retracting), the device will overshoot the desired position by 640 microsteps (assuming 64 microsteps/step), reverse direction and approach the requested position from below. On positive moves (extending), the device behaves normally. Care must be taken not to crash the moving payload into a fixed object due to the 640 microsteps overshoot on negative moves. The default value is 0 on all devices. See note on anti-backlash and anti-sticktion below. * |
| bit_2 | 4 | Enable Anti-sticktion Routine A value of 1 enables the anti-sticktion routine. On moves less than 640 microsteps (assuming 64 microsteps/step), the device will first retract to a position 640 microsteps less than the requested position and approach the requested position from below. Care must be taken not to crash the moving payload into a fixed object due to the 640 microsteps negative move. The default value is 0 on all devices. See section on anti-backlash and anti-sticktion below this table. * |
| bit_3 | 8 | Disable Potentiometer A value of 1 disables the potentiometer preventing manual adjustment of the device. The default value is 0 on all devices. |
| bit_4 | 16 | Enable Move Tracking A value of 1 enables the Move Tracking response during move commands. The device will return its position periodically when a move command is executed. The Disable Auto-Reply option above takes precedence over this option. The default value is 0 on all devices. Before firmware version 5.14, only Move at Constant Speed commands could generate tracking responses, now all move commands can. |
| bit_5 | 32 | Disable Manual Move Tracking A value of 1 disables the Manual Move Tracking response during manual moves. The Disable Auto-Reply option above takes precedence over this option. The default value is 0 on all devices. |
| bit_6 | 64 | Enable Message IDs A value of 1 enables Message IDs. In this mode of communication, only bytes 3 through 5 are used for data. Byte 6 is used as an ID byte that the user can set to any value they wish. It will be returned unchanged in the reply. Message IDs allow the user's application to monitor communication packets individually to implement error detection and recovery. The default value is 0 on all devices. Prior to firmware version 5.06, this feature was called "Virtual Channels Mode" and did not behave reliably. We do not recommend enabling this mode of communications unless you have firmware version 5.06 or later. |
| bit_7 | 128 | Home Status This bit is set to 0 automatically on power-up or reset. It is set automatically when the device is homed or when the position is set using command #45. It can be used to detect if a device has a valid position reference. It can also be set or cleared by the user. |
| bit_8 | 256 | Disable Auto-Home A value of 1 disables auto-home checking. Checking for trigger of home sensor is only done when home command is issued. This allows rotational devices to move multiple revolutions without re-triggering the home sensor. |
| bit_9 | 512 | Reverse Potentiometer A value of 1 reverses the direction of the travel when the potentiometer is used to control the device. This mode bit was introduced in firmware version 5.06. Prior to that it was not used. |
| bit_10 | 1,024 | Reserved |
| bit_11 | 2,048 | Microstepping Mode A value of 1 enables circular phase microstepping. A value of 0 enables square phase microstepping mode. The differences are: Circular Phase:
Square Phase:
|
| bit_12 | 4,096 | Set Home Switch Logic The T-CD series can accept a variety of motors and home sensors. Some devices have active high home limit switches. On these devices, this bit must be changed from the default setting in order for the home sensor to function correctly. A value of 1 must be set for these devices for the device to home properly. Damage to the home sensor or actuator may result if this bit is set improperly. |
| bit_13 | 8,192 | Reserved |
| bit_14 | 1,6384 | Disable Power LED A value of 1 turns off the green power LED. It will still blink briefly, immediately after powerup. |
| bit_15 | 32,768 | Disable Serial LED A value of 1 turns off the yellow serial LED. |
*Anti-backlash and Anti-sticktion routines are designed to compensate for backlash and sticktion. The solution to backlash is to always approach a position from the same direction. The solution to sticktion is to move the device far enough away from the final position to break free of sticktion before attempting the final move. The operation of the two features are dependent on each other, and the interaction of enabling one or both of the features is described in the diagram to the right.
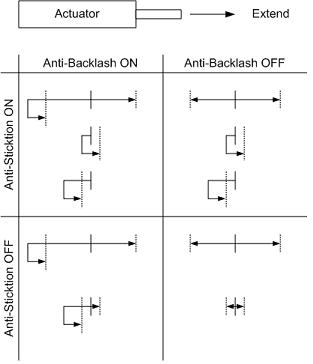
For each setting scenario, the starting position is denoted by the solid vertical line and the final position is denoted by the dotted vertical line. There are four possible moves for each scenario: long move positive, long move negative, short move positive and short move negative. The arrows show the path that would be traversed for each scenario.
Set Target Speed - Cmd 42
| Instruction Name | Set Target Speed |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 42 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Speed |
| Reply Data | Speed |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Sets the speed at which the device moves when using the "Move Absolute" or "Move Relative" commands. |
When a move absolute or move relative instruction is issued, the device will accelerate at a rate determined by the acceleration setting up to the speed determined by this command.
The target velocity may be changed on-the-fly even when the device is in the middle of a move. The device will automatically adjust the velocity, but still target the final position specified in the original move.
For a spreadsheet that can be used to calculate speed setting values for any product see https://www.zaber.com/documents/ZaberSpeedSetting.xls. Alternatively you may use the formulas below.
Actual Speed
- = Data * 9.375 * M mm/s or deg/s
- = Data * 9.375 microsteps/s
- = Data * 9.375 / R steps/s
- = Data * 9.375 / (R x S) * 60 revolutions/min Motor rpm
- = Data * 9.375 * L / (R x S) mm/s Linear devices only
where:
- Data is the value of the command data
- R (microsteps/step) is the microstep resolution (command 37)
- S (steps/revolution) is the number of steps per motor revolution
- M (mm or deg) is the microstep size
- L (mm or deg) is the distance of linear motion per motor revolution
Refer to product specifications for the distance corresponding to a single microstep or revolution.
For example, if a motor has 48 steps per revolution (S = 48), used with default resolution (R = 64), and Data is 2922, then the motor will move at a speed of approximately 535 revolutions per minute.
Valid data values are from 0 to (512×R−1). In Firmware 5.21 and 5.22, a value of 0 is not allowed. In all other versions, target speed of 0 will cause Move Absolute/Relative and Move to Stored Position commands to return an error.
Set Acceleration - Cmd 43
| Instruction Name | Set Acceleration |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 43 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Acceleration |
| Reply Data | Acceleration |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Sets the acceleration used by the movement commands. |
When a movement command is issued, the device will accelerate at a rate determined by this command "Set Acceleration" up to a maximum speed determined by the target velocity. The acceleration may be changed on-the-fly even when the device is in the middle of a move. To determine the acceleration that will result from a given data value, the following formulas may be used:
- Actual Acceleration
- = 11250 * Data * M mm/s^2 or deg/s^2
- = 11250 * Data microsteps/s^2
- = 11250 * Data / R steps/s^2
Where:
- Data is the value specified in the Command Data
- M (mm or deg) is the microstep size
- R is the microstep resolution set in command #37 (microsteps/step)
The maximum value allowable is (512*R-1). This is the same as the maximum allowable data for velocity, which means that the device will reach maximum velocity immediately. If acceleration is set to 0, it is as if acceleration is set to (512*R-1). Effectively acceleration is turned off and the device will start moving at the target speed immediately.
Set Maximum Position - Cmd 44
| Instruction Name | Set Maximum Position |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 44 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Range |
| Reply Data | Range |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Sets the maximum position the device is allowed to travel to. |
Use this command to limit the range of travel to a value other than the default. Exercise caution when using this command, since it is possible to set the range to a value greater than the physical limits of the device.
A device within range of travel is not allowed to move above its Maximum Position. Valid values can be any number from 0 to 16777215.
The behaviour of this command depends on the firmware version:
- 5.01 - 5.20
Device movement behaviour when out of range is not well-defined.
- 5.21 - 5.22
The new Maximum Position cannot be less than the current position.
- 5.23 and up
If the device Current Position is out of range and above Maximum Position, the device is not allowed to move in the positive direction.
This setting is stored in non-volatile memory and will persist after power-down or reset.
NOTE: This command was previously named Set Maximum Range.
Set Current Position - Cmd 45
| Instruction Name | Set Current Position |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 45 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | New Position |
| Reply Data | New Position |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | Yes |
| Persistence | Volatile |
| Summary | Sets the device internal position counter. |
This command override the internal position counter with a new position value specified by the user.
The position data is volatile and will not persist after power-down or reset.
The phase of the stepper motor is controlled by the least significant byte of the position, thus the device may move by +/- 2 full steps unless the new position corresponds to the true current position of the device. This command is useful if you want to turn off the system without losing position. Simply save the position in the controlling computer and turn off the hold current (Command 39) before powering down. After powering up, set the position back to the saved value and turn on the hold current. In this way you can continue without having to home the device. You have to turn off the hold current because when the power first comes on the position will default to the maximum range, and that may be out of phase with the motor's current position. If the hold current is on, it will force the motor into phase with the default position before you've had a chance to restore the current position.
In Firmware 5.21 and 5.22, the new Current Position must be equal or less than Maximum Position. See Set Maximum Position (Cmd 44) for more details on range settings and behaviour.
Set Maximum Relative Move - Cmd 46
| Instruction Name | Set Maximum Relative Move |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 46 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Range |
| Reply Data | Range |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-volatile |
| Summary | Sets a limit on the number of microsteps the device can make for a Relative Move command. |
Use this command to limit the maximum range of travel for a relative move command. For example, if maximum relative move is set to 1000, and the user requests a relative move (#21) of 800, then the device will move 800 microsteps. However, if the user requests a relative move of 1200, then the device will reply with an error code. Most applications can leave this unchanged from the default.
This setting is stored in non-volatile memory and will persist after power-down or reset.
Set Home Offset - Cmd 47
| Instruction Name | Set Home Offset |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 47 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Offset |
| Reply Data | Offset |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Sets the the new "Home" position which can then be used when the Home command is issued. |
When the home command is issued, the device will retract until the home sensor is triggered, then move forward until the home sensor is no longer triggered, then move forward by the Home Offset value (in microsteps) and resets the internal position (to 0 for most devices).
Note that the home offset command also changes the range settings of the device. For example, if the initial Home Offset is 0 and the Maximum Position is 500,000, and the user changes the Home Offset to 70,000, then the Maximum Position is automatically adjusted to be 430,000. However, changing the Maximum Position does not affect the home offset.
When a new Home Offset is specified, Maximum Position is adjusted to provide the same maximum location. However, the device will not be able to travel below its new home position unless it is homing.
This setting is stored in non-volatile memory and will persist after power-down or reset.
Set Alias Number - Cmd 48
| Instruction Name | Set Alias Number |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All Zaber devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.00 and up |
| Command Number | 48 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Alias Number |
| Reply Data | Alias Number |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Sets an alternate device number for a device. |
This setting specifies an alternate device number for a device (in addition to its actual device number). By setting several devices to the same alias number, you can control a group of devices with a single instruction. When you send an instruction to an alias number, all devices with that alias number will execute the instruction and reply using their actual device numbers. To remove an alias, simply set the device's alias number to zero. Valid alias numbers are 0 to 99 for version 6.05, and 0 to 254 otherwise. To avoid confusion, it is best to choose an alias greater than the number of devices connected.
This setting is stored in non-volatile memory and will persist after power-down or reset.
Set Lock State - Cmd 49
| Instruction Name | Set Lock State |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx since 5.07 |
| Command Number | 49 |
| Command Type | Setting |
| Command Data | Lock State |
| Reply Data | Lock State |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | Non-Volatile |
| Summary | Locks or unlocks all non-volatile settings. |
Sometimes it is desirable to lock all non-volatile settings to prevent them from being changed inadvertently. After changing all settings as desired, settings can be locked by setting the Lock State to 1. Subsequent attempts to change any non-volatile setting (e.g., Set Target Speed, command 42) will result in an error response with an error code of 3600 (settings locked). Note that the Set Lock State command does not apply to commands and settings that are specific to the T-JOY3 joystick. Load Event Instruction and Set Axis Device Number for example, are unaffected by the Lock State.
How the Restore Settings instruction behaves when the settings are locked depends on the firmware version. In version 5.07 issuing a Restore Settings instruction while the settings are locked will result in an error response with an error code of 3600 (settings locked). This behavior was found to confuse many customers so in version 5.08 and up, the behavior was changed such that regardless of the current lock state, issuing a Restore Settings instruction will always return setting values to factory default values and leave settings in an unlocked state.
Settings can also be unlocked by setting the Lock State to 0.
Return Device ID - Cmd 50
| Instruction Name | Return Device ID |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All Zaber devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.00 and up |
| Command Number | 50 |
| Command Type | Read-Only Setting |
| Command Data | Ignored |
| Reply Data | Device ID |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Returns the ID number for the type of device connected. |
See the Zaber support web site for a table of device IDs for all Zaber products.
Return Firmware Version - Cmd 51
| Instruction Name | Return Firmware Version |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All Zaber devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.00 and up |
| Command Number | 51 |
| Command Type | Read-Only Setting |
| Command Data | Ignored |
| Reply Data | Version |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Returns the firmware version installed on the device. |
A decimal is assumed before the last two digits. For example, 502 indicates firmware version 5.02.
Return Power Supply Voltage - Cmd 52
| Instruction Name | Return Power Supply Voltage |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All Zaber devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.00 and up |
| Command Number | 52 |
| Command Type | Read-Only Setting |
| Command Data | Ignored |
| Reply Data | Voltage |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Returns the voltage level of the device's power supply. |
A decimal is assumed before the last digit. For example, a value of 127 indicates 12.7 V. Note that the internal voltage measurement is not very accurate. Don't be alarmed if the indicated voltage is slightly different from your measurements.
Return Setting - Cmd 53
| Instruction Name | Return Setting |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All Zaber devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.00 and up |
| Command Number | 53 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Setting Number |
| Reply Data | Setting Value |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Returns the current value of the setting specified in the Command Data. |
Valid command data values are the command numbers of any "Set..." instruction. The device will reply using the command number of the specified setting (as if a command to change the setting had just been issued) but the setting will not be changed.
For example, command #48 is the "Set Alias" instruction. Therefore if you wish to return the current value of the alias number, simply send the Return Setting instruction with data of 48. The device will reply with command #48 and data equal to the setting value.
Since firmware version 5.21, this command also accepts the command numbers of any "Return..." instruction, such as command #50 "Return Device ID".
Return Status - Cmd 54
| Instruction Name | Return Status |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 54 |
| Command Type | Read-Only Setting |
| Command Data | Ignored |
| Reply Data | Status |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Returns the current status of the device. |
Possible status codes are as follows:
- 0 - idle, not currently executing any instructions
- 1 - executing a home instruction
- 10 - executing a manual move (i.e. the manual control knob is turned)
- 18 - executing a move to stored position instruction (FW 5.04 and up only)
- 20 - executing a move absolute instruction
- 21 - executing a move relative instruction
- 22 - executing a move at constant speed instruction
- 23 - executing a stop instruction (i.e. decelerating)
Echo Data - Cmd 55
| Instruction Name | Echo Data |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All Zaber devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.04 and up |
| Command Number | 55 |
| Command Type | Command |
| Command Data | Data |
| Reply Data | Data |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Echoes back the same Command Data that was sent. |
This command is useful for testing communication, similar to a network "ping".
Return Current Position - Cmd 60
| Instruction Name | Return Current Position |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.00 and up |
| Command Number | 60 |
| Command Type | Read-Only Setting |
| Command Data | Ignored |
| Reply Data | Position |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | Yes |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Returns the current absolute position of the device in microsteps. |
This is equivalent to issuing a Return Setting (#53) command with a command data value of 45 (Set Current Position).
Reply-Only Reference
In general, a Zaber device will reply to an instruction using the same command number as the instruction itself. However, there are occasions (such as when the user turns a manual control knob) when the device may transmit data without first receiving a request from the controlling computer. This type of reply may be considered to be a triggered reply as opposed to a requested reply. In this case the device uses a “reply-only” command number to distinguish the reply from those requested by the controlling computer. The meanings of these replies and their corresponding data are given below.
Move Tracking - Cmd 8
| Instruction Name | Move Tracking |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 8 |
| Command Type | Reply |
| Command Data | n/a |
| Reply Data | Position |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | Yes |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Indicates to the user that the device has been set to a position tracking mode and given a move instruction. |
Move Tracking has been enabled (see Set Device Mode (Cmd 40)) and device has been given a move instruction. In this mode, the device sends this reply every 0.25 seconds updating the current absolute position (in microsteps) during any move.
Limit Active - Cmd 9
| Instruction Name | Limit Active |
|---|---|
| Applies to | All motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.00 and up |
| Command Number | 9 |
| Command Type | Reply |
| Command Data | n/a |
| Reply Data | Position |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | Yes |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Indicates to the user that the device has reached one of the limits of travel. |
This response from a device indicates that a “move at constant speed” command has finished. Generally this is because the device reached one of the limits of travel (either the minimum position or maximum position), but it also occurs if the device is ordered to move at constant speed zero.
Manual Move Tracking - Cmd 10
| Instruction Name | Manual Move Tracking |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 10 |
| Command Type | Reply |
| Command Data | n/a |
| Reply Data | Position |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | Yes |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | A reply that is sent when the manual control knob is turned. |
Manual Move Tracking has been enabled (see Set Device Mode (Cmd 40)) and the device has been moved manually (the knob is turned). In this mode, the device sends this reply every 0.25 seconds updating the current absolute position (in microsteps) during any move.
Error - Cmd 255
| Instruction Name | Error |
|---|---|
| Applies to | T-Series motorized devices |
| Firmware Version | 5.xx |
| Command Number | 255 |
| Command Type | Reply |
| Command Data | n/a |
| Reply Data | Error Code |
| Safe to retry? | Yes |
| Returns Current Position? | No |
| Persistence | n/a |
| Summary | Indicates to the user that an error has occurred. |
This reply indicates that an error has occurred. The error code returned in the data indicates the type of error. The device may send an error code as a reply to an invalid instruction, or it may autonomously send an error code as a triggered reply (i.e. not in response to an instruction). The error code is typically the command number of the instruction that caused the error, but not always.
Error Codes
| Code | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cannot Home | Home - Device has traveled a long distance without triggering the home sensor. Device may be stalling or slipping. |
| 2 | Device Number Invalid | Renumbering data out of range. |
| 14 | Voltage Low | Power supply voltage too low. |
| 15 | Voltage High | Power supply voltage too high. |
| 18 | Stored Position Invalid | The position stored in the requested register is no longer valid. This is probably because the maximum range was reduced. |
| 20 | Absolute Position Invalid | Move Absolute - Target position out of range. |
| 21 | Relative Position Invalid | Move Relative - Target position out of range. |
| 22 | Velocity Invalid | Constant velocity move. Velocity out of range. |
| 36 | Peripheral Id Invalid | Restore Settings - peripheral id is invalid. Please use one of the peripheral ids listed in the user manual, or 0 for default. |
| 37 | Resolution Invalid | Invalid microstep resolution. Resolution may only be 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128. |
| 38 | Run Current Invalid | Run current out of range. See command 38 for allowable values. |
| 39 | Hold Current Invalid | Hold current out of range. See command 39 for allowable values. |
| 40 | Mode Invalid | Set Device Mode - one or more of the mode bits is invalid. |
| 41 | Home Speed Invalid | Home speed out of range. The range of home speed is determined by the resolution. |
| 42 | Speed Invalid | Target speed out of range. The range of target speed is determined by the resolution. |
| 43 | Acceleration Invalid | Target acceleration out of range. The range of target acceleration is determined by the resolution. |
| 44 | Maximum Range Invalid | The maximum range may only be set between 1 and the resolution limit of the stepper controller, which is 16,777,215. |
| 45 | Current Position Invalid | Current position out of range. Current position must be between 0 and the maximum range. |
| 46 | Maximum Relative Move Invalid | Max relative move out of range. Must be between 0 and 16,777,215. |
| 47 | Offset Invalid | Home offset out of range. Home offset must be between 0 and maximum range. |
| 48 | Alias Invalid | Alias out of range. |
| 49 | Lock State Invalid | Lock state must be 1 (locked) or 0 (unlocked). |
| 53 | Setting Invalid | Return Setting - data entered is not a valid setting command number. Valid setting command numbers are the command numbers of any "Set ..." instructions. |
| 64 | Command Invalid | Command number not valid in this firmware version. |
| 255 | Busy | Another command is executing and cannot be pre-empted. Either stop the previous command or wait until it finishes before trying again. |
| 1600 | Save Position Invalid | Save Current Position register out of range (must be 0-15). |
| 1601 | Save Position Not Homed | Save Current Position is not allowed unless the device has been homed. |
| 1700 | Return Position Invalid | Return Stored Position register out of range (must be 0-15). |
| 1800 | Move Position Invalid | Move to Stored Position register out of range (must be 0-15). |
| 1801 | Move Position Not Homed | Move to Stored Position is not allowed unless the device has been homed. |
| 2146 | Relative Position Limited | Move Relative (command 20) exceeded maximum relative move range. Either move a shorter distance, or change the maximum relative move (command 46). |
| 3600 | Settings Locked | Must clear Lock State (command 49) first. See the Set Lock State command for details. |
| 4008 | Disable Auto Home Invalid | Set Device Mode - this is a linear actuator; Disable Auto Home is used for rotary actuators only. |
| 4010 | Bit 10 Invalid | Set Device Mode - bit 10 is reserved and must be 0. |
| 4012 | Home Switch Invalid | Set Device Mode - this device has integrated home sensor with preset polarity; mode bit 12 cannot be changed by the user. |
| 4013 | Bit 13 Invalid | Set Device Mode - bit 13 is reserved and must be 0. |